Introduction:
Stem cells have captivated the imagination of scientists and the public alike for their remarkable potential to revolutionize medicine. These unique cells possess the extraordinary ability to develop into many different cell types in the body, offering a promising avenue for regenerative medicine, disease treatment, and understanding human development.
Stem cells: What Are They?
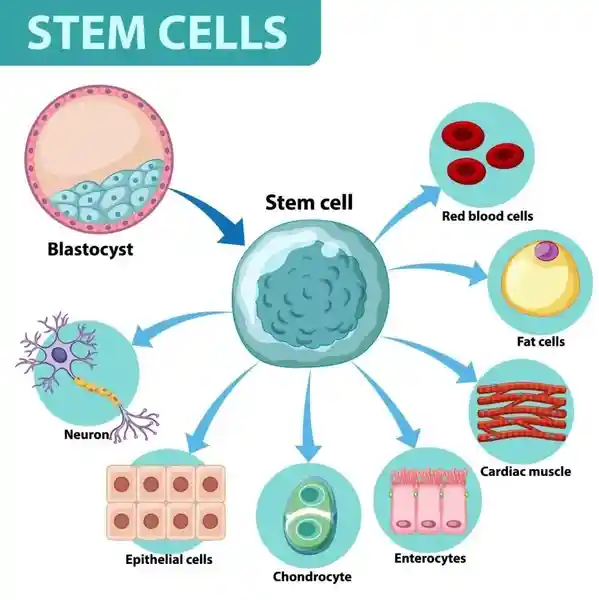
With the ability to self-renew and develop into distinct cell types, stem cells are undifferentiated cells. The ability to divide and create more specialized cell types as well as identical clones of themselves is what distinguishes them. This special characteristic enables stem cells to function as the body’s repair mechanism, regenerating other cells for as long as an individual is alive.
Two major categories exist for stem cells. They are two types of stem cells: adult and embryonic. Neural progenitor cells. Today’s research uses embryonic stem cells derived from discarded embryos. These are the outcome of the process of in vitro fertilization.
There are several main categories: The “pluripotent” stem cells (embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells) and nonembryonic or somatic stem cells (commonly called “adult” stem cells).
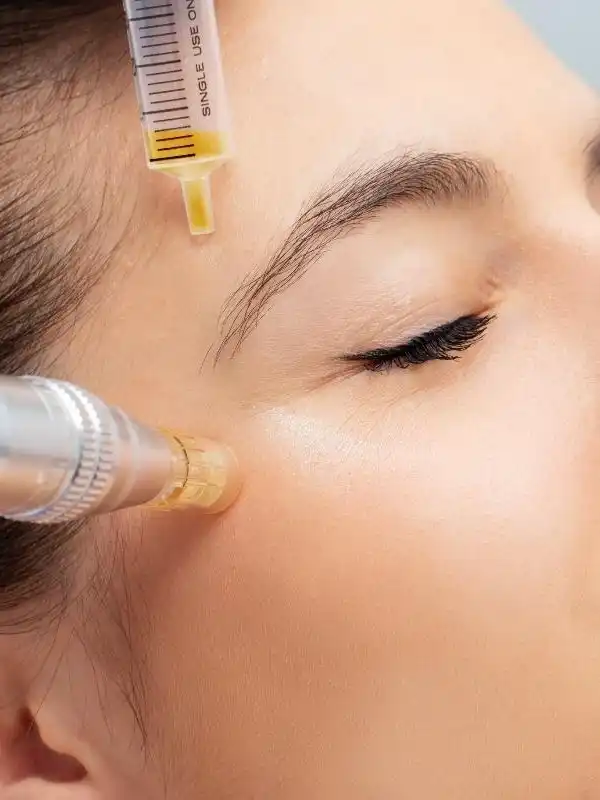
Cosmetic uses of Stem Cells:
Due to its potential to regenerate skin, lessen indications of aging, and enhance general skin health, stem cell applications for cosmetic purposes have attracted a lot of interest recently. The healing qualities of stem cells, especially those produced from bone marrow and adipose tissue (fat), make them useful in cosmetic operations. Below are a few typical applications of stem cells in cosmetics:
Anti-Aging Remedies:
Skin sagging, fine lines, and wrinkles can all be lessened with stem cell-based therapy.
Collagen and elastin, which are necessary for preserving the suppleness and rigidity of skin, are produced more readily by stem cells.
Skin Rejuvenation:
By promoting cell renewal and regeneration, stem cells can enhance the tone, texture, and general look of the skin.
They can aid in restoring damaged skin cells and enhancing the suppleness and moisture of the skin.

Hair Growth:
In hair transplant treatments, stem cells are employed to increase hair density and encourage the formation of hair follicles.
They can also aid in the restoration of damaged hair follicles and enhance the scalp’s general health.
Scar Healing:
Through tissue remodeling and regeneration, stem cells can help lessen the visibility of scars, particularly acne scars.
Additionally, they might lessen the visibility of scar tissue by enhancing its elasticity and texture.
Kinds of stem cells:
Multiple varieties of stem cells exist, each possessing distinct characteristics and possible uses. Stem cells mostly come in two varieties:
Embryonic stem cells:
Cells that are produced from the core mass of growing embryos are known as embryonic stem cells, or ESCs. They can develop into any form of cell in the body because they are pluripotent. Because ESCs may mimic human development and have potential applications in regenerative medicine, they are frequently employed in research.
Obtained usually from leftover embryos during in vitro fertilization operations, from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst-stage embryo.
They can differentiate into any form of cell in the body because they are pluripotent.
In order to better understand embryonic development, simulate diseases, and create possible remedies for a range of medical disorders, ESCs are widely employed in research.
Adult stem cells
They are undifferentiated cells, found throughout the body after development that multiply by cell division to replenish dying cells and regenerate damaged tissues. Also known as somatic stem cells, they can be found in juvenile, adult animals, and humans, unlike embryonic stem cells.
Found in particular body organs and tissues, including the muscles, liver, brain, skin, and bone marrow.
They have the capacity to differentiate into a restricted spectrum of cell types associated with their original tissue, making them multipotent or occasionally unipotent.
Adult stem cells support the body’s inherent healing mechanisms by playing critical roles in tissue maintenance, repair, and regeneration.
Induced pluripotent stem cells:
A type of stem cell known as induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) is created in a lab by reprogramming adult cells, including skin or blood cells, to become pluripotent again. Comparable to embryonic stem cells (ESCs), pluripotent stem cells possess the amazing capacity to develop into any type of cell in the body; however, they are not formed from embryos.
Perinatal Stem Cells:
These stem cells are found in umbilical cord blood, umbilical cord tissue, and the placenta. They include umbilical cord blood stem cells (UCBSCs), amniotic fluid stem cells (AFSCs), and placental stem cells (PSCs). Perinatal stem cells are multipotent and can differentiate into various cell types.
Derived from tissues related to birth, such as placental, umbilical cord, and blood tissue.
For use in transplantation and regenerative medicine down the road, these stem cells can be stored and cryopreserved after being acquired non-invasively.
Adoptive stem cells encompass mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), and other progenitor cells possessing potential for therapeutic applications.
Mesenchymal stem cells:
Adult stem cells known as mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are present in the bone marrow, adipose tissue (fat), and umbilical cord tissue, among other tissues and organs. Because MSCs are multipotent, they possess the capacity to differentiate into many cell types, such as adipocytes, chondrocytes, and osteoblasts, which are cells found in cartilage, bones, and other tissues.
Hematopoietic stem cells:
The potential use of hematopoietic stem cells in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine are also being investigated. Scientists are looking on ways to modify HSCs so they can produce particular blood cell types or fix damaged organs and tissues.
All things considered, hematopoietic stem cells are an essential part of the body’s ability to regenerate itself and have enormous potential to advance medical science and enhance therapies for a variety of illnesses.
Functions of stem cells:
Tissue mend and Regeneration: The capacity of stem cells to renew and mend damaged tissues is one of their best-known uses. Stem cells have the ability to differentiate into specific cell types in response to injury or normal wear and strain on tissues. This process replaces lost or damaged cells and aids in the restoration of tissue structure and function.
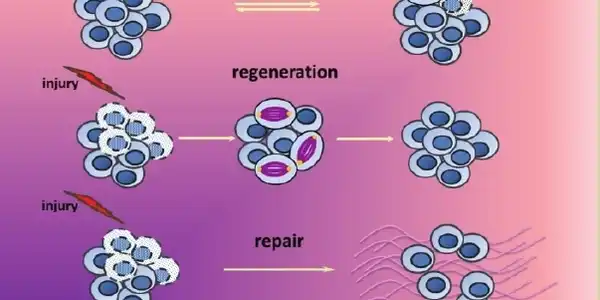
Preservation of Tissue Homeostasis:
By continuously repopulating the reservoir of specialized cells found within tissues and organs, stem cells help preserve tissue homeostasis. Stem cells ensure the long-term integrity and function of tissues by dividing and producing more stem cells through a process known as self-renewal.
Development and Growth:
All of the various cell types and tissues that make up the body are derived from stem cells during the embryonic stage of development. With their capacity to differentiate into any form of cell, pluripotent stem cells—including embryonic stem cells—offer the building blocks necessary for organogenesis and embryonic development.
Immune Response:
By producing specialized immune system cells including T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells, stem cells contribute to the regulation of the immunological response. The bone marrow contains hematopoietic stem cells, which are the source of blood cells, including immune cells that fight infections and illnesses.
Extended Lifespan and Aging:
The aging process and longevity have been linked to stem cells. Because stem cells lose some of their ability to regenerate, aging-related disorders become more likely to strike and tissue repair becomes less effective. The goal of aging research is to comprehend how stem cell function varies with age.
Stem cells are useful tools for researching disease causes, evaluating possible medicines, and creating novel treatments. These applications include disease modeling and drug discovery. Researchers are able to assess the effectiveness of medications and simulate disease pathology in a controlled laboratory environment by isolating patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from patients with hereditary disorders.
Regenerative Medicine:
A variety of illnesses and injuries, such as neurological conditions, cardiovascular conditions, musculoskeletal injuries, autoimmune diseases, and spinal cord injuries, may be treated with stem cell-based therapies. Through the use of stem cells’ regenerative potential, scientists hope to create novel therapies that enhance patient outcomes and quality of life.
Applications of stem cells:
Regenerative medicine:
By using stem cells to repair damaged tissues and organs, diseases like diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, and heart disease may be cured.
Illness Modeling:
In vitro human illness modeling can be greatly aided by stem cells, especially induced pluripotent stem cells (IPSCs). Patients with genetic abnormalities can be used to create IPSCs, which enables researchers to examine disease mechanisms, pinpoint therapeutic targets, and evaluate possible medications in a regulated setting. Numerous illnesses, such as diabetes, uncommon genetic syndromes, cardiovascular problems, and neurodegenerative diseases, have disease-specific iPSC models developed.
Drug Discovery and Screening:
Using stem cell-based models, researchers can assess the safety and effectiveness of possible treatments. This provides a platform for drug discovery and screening. A more physiologically realistic method for assessing drug candidates is offered by stem cell-derived tissues and organoids, which more closely resemble the complexity of human tissues than conventional cell culture models. These models are useful for prioritizing compounds for more research, predicting therapeutic reactions, and identifying prospective drug candidates.
Cell replacement Therapy:
Treating a variety of illnesses and wounds with stem cell transplantation shows promise since it replaces unhealthy or malfunctioning cells with functional, healthy ones. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, for instance, replaces the patient’s blood cell supply with healthy donor cells in order to treat blood malignancies like leukemia and lymphoma.
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Dentistry:
Tissue engineering techniques use stem cells to build scaffolds or three-dimensional constructions that closely resemble the composition and capabilities of natural tissues and organs. Applications in wound healing, transplantation, and regenerative dentistry are possible for these created tissues. For instance, dental pulp stem cells are being studied for their ability to repair dental illnesses and injuries by regenerating dental tissues like dentin, pulp, and periodontal ligament.
Cosmetic Aesthetic medicine:
The use of stem cells in cosmetic and aesthetic operations for hair restoration, face enlargement, and skin rejuvenation is growing. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and adipose-derived stem cell therapies are two examples of stem cell-based products that are used to increase the production of collagen, enhance skin texture, and encourage tissue regeneration. These treatments can help reduce wrinkles, enhance facial volume, and address hair loss, offering natural-looking results with minimal downtime.
Bioprocessing and Bio manufacturing:
The creation of cell-based medicines, vaccines, and biologics is facilitated by the use of stem cells in bioprocessing and bio manufacturing applications. In order to generate vast amounts of cells or cell-derived products for use in medicine, stem cell cultures can be expanded and modified. Therapeutic cells and tissues can now be produced effectively and economically because to developments in stem cell bioprocessing methods such suspension culture systems and bioreactor technology.
Moral Aspects to Take into Account
Ethical questions are raised by the use of stem cells in research and treatment, especially when using embryonic stem cells. Since the destruction of embryos to acquire ESCs has been a contentious issue, ethical substitutes like iPSCs have been developed. Nevertheless, ethical issues are still a big part of stem cell research and treatment.
Technical and practical methods of harvesting stem cells from fat and serum/blood:
Isolating Stem Cells from Adipose Tissue and Fat:
Liposuction process: A liposuction process is the most widely used technique for obtaining adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs). A tiny incision is created, and a cannula is introduced to remove fat from the buttocks, thighs, and belly.
Handling the Fat: In order to separate the stem cells, the obtained fat tissue is treated. To release the stem cells and break down the extracellular matrix, this may require enzymatic digestion. After filtering and centrifuging the mixture, the stem cells are separated from the remaining ingredients.
Isolating and Concentrating Stem Cells: To improve their potency and efficacy, the isolated stem cells are subsequently concentrated. There are several uses for this concentrated stem cell solution, including tissue
Extracting Peripheral Blood Serum/Blood Stem Cells:
Stem cell extraction from peripheral blood is another method for obtaining stem cells. This is causing the bone marrow to release stem cells into the bloodstream in the periphery. To increase stem cell synthesis, the patient is administered granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, or G-CSF.
The process known as apheresis is used to gather the stem cells after they are discharged into the peripheral circulation. Following the patient’s blood draw, the stem cells are separated by a machine and the blood is subsequently put back into the patient.
Its Benefits:
Rich Source of Stem Cells: Melanchymal stem cells (MSCs) found in fat and hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) found in peripheral blood are two particularly abundant sources of stem cells.
Minimally Invasive: Compared to surgical methods, the extraction of stem cells from fat and serum/blood is less invasive, negating the need for prolonged recuperation and lowering the risk of problems.
Reducing the possibility of rejection or allergic responses, the extracted stem cells are natural and autologous, originating from the patient’s own body.
Tissue regeneration, anti-aging therapies, and wound healing are all made possible by stem cells’ regenerative and restorative qualities.
Versatility: A variety of cell types can be differentiated from stem cells obtained from fat and serum/blood, providing a wide range of potential applications in regenerative medicine.
Why it works:
Because stem cells possess special regenerative qualities, stem cell-based cosmetic treatments are effective. Because stem cells may develop into multiple cell types and encourage tissue regeneration, they are perfect for restoring and regenerating damaged skin. The following explains the efficacy of stem cell-based cosmetic treatments.
Cell Renewal and Regeneration: Stem cells stimulate the production of new skin cells, replacing damaged or aging cells. This process improves skin texture, tone, and overall appearance.
Collagen and Elastin Production: Stem cells promote the production of collagen and elastin, which are essential proteins for maintaining skin elasticity and firmness. Increased collagen and elastin levels result in smoother, tighter skin with fewer wrinkles and fine lines.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Stem cells have anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce redness, swelling, and irritation in the skin. This can improve the appearance of skin conditions such as acne, rosacea, and eczema.
Enhanced Skin Hydration: Stem cells help improve skin hydration by promoting the production of hyaluronic acid, a natural moisturizer that helps keep skin plump and hydrated.
Improved Wound Healing: Stem cells accelerate the healing process of wounds, cuts, and abrasions by promoting the regeneration of skin cells and tissues.
Reduction of Scars and Pigmentation: Stem cells can help reduce the appearance of scars, including acne scars, by promoting tissue regeneration and remodeling. They can also help lighten skin tone and reduce hyperpigmentation.
Hair Regrowth: In hair restoration procedures, stem cells stimulate hair follicle growth and improve hair density. They can also repair damaged hair follicles and improve scalp health.
Long-lasting Results: Stem cell-based treatments offer long-lasting results compared to traditional cosmetic procedures. This is because stem cells promote natural, gradual improvements in skin health and appearance.
Many patients prefer stem cell-based cosmetic procedures over standard tissue fillers because of their many advantages. Among the main advantages are:
Natural Results: Because stem cell therapy activates the body’s innate mechanisms of cell renewal and regeneration, the effects appear natural. As a consequence, skin seems renewed and invigorated without coming off as too dramatic or unnatural.
Long-Lasting Effects: Unlike conventional tissue fillers, stem cell-based treatments provide long-lasting outcomes. This is so that the skin’s look can gradually improve over time as stem cells encourage the creation of new, healthy skin cells.
Better Skin Texture and Tone: By promoting the development of collagen and elastin, stem cell-based therapies can enhance the texture and tone of the skin. As a result, the skin becomes firmer and smoother, with less fine lines and wrinkles.
Versatility: A wide range of cosmetic issues, such as wrinkles, fine lines, sagging skin, and uneven skin tone, can be addressed using stem cell-based treatments. Their adaptability renders them appropriate for an extensive range of patients and skin types.
Natural Ingredients: The natural components used in stem cell treatments come from ethically sourced donors or the patient’s own body. By doing this, the possibility of allergic responses and other negative effects is decreased.
Why Stem Cell-Based Treatments are better than Typical Tissue Fillers:
Traditional tissue fillers can temporarily improve the appearance of the skin, but stem cell-based therapies provide a number of benefits:
Longevity: Compared to standard tissue fillers, which may require repeated procedures to maintain results, stem cell-based therapies offer longer-lasting outcomes.
Regenerative Properties: Rather than merely temporarily smoothing away wrinkles or lines, stem cell-based therapies have the ability to regenerate skin cells, which can enhance the skin’s general health and look.
Natural Appearance: Because stem cell-based therapies encourage the body’s natural processes of skin regeneration and repair, they result in a more natural appearance.
Safety: There is little chance of negative side effects or consequences with stem cell-based therapies, which are widely regarded as safe. They are therefore a good choice for a lot of patients.
Comparing Surgical Implants and Generic Synthetic Temporary

Duration of Outcomes:
Treatments Utilizing Stem Cells: Because of their capacity for regeneration, these treatments yield enduring effects. As the health and look of the skin are improved over time, the results may get better still.
Generic Synthetic Temporary Fillers:
Provide short-term effects, usually lasting a few months to a year. It normally takes more than one treatment to keep the results.
Long-lasting results can be obtained with surgical implants, but they are irreversible and might not adjust over time to changes in the surrounding tissues.
Natural Look:
Stem cell-based treatments encourage the body’s natural processes of regeneration and repair while producing results that look natural.
Synthetic Temporary Fillers: When used excessively or improperly injected, they may occasionally give off a visible or unnatural appearance.
Surgical implants:
Depending on the patient’s objectives, these may or may not result in a perceptible change in appearance.
Security:
Treatments Using Stem Cells: These are generally regarded as safe, particularly when using autologous stem cells, which are taken from the patient’s own body.
Temporary synthetic fillers that are generic: They are generally safe, but there is a chance of allergic responses or other negative side effects.
Complications from surgical implants, such as infection, implant rejection, or implant migration, are more common.

Rest and Recuperation:
Treatments Using Stem Cells: These usually involve little recovery time, so patients can quickly resume their regular activities.
Temporary Synthetic Fillers: These usually cause little recovery time, however they can cause minor bruising or swelling.
Surgical implants: These frequently entail a lengthier recuperation period, activity limitations, and the possibility of more severe side effects.
Cost: Treatments Using Stem Cells: Due to their longevity, these treatments may be more expensive initially but less expensive over time.
Temporary fillers made of synthetic generics are typically less expensive up front, but they need to be repeated, which might mount up over time.
Surgical implants can be expensive, particularly when you include in the price of anesthesia, the procedure, and the recovery period.
Personalization and Adaptability:
Stem cell-based treatments are versatile and may be tailored to each patient’s unique needs, addressing a wide range of skin issues.
Temporary synthetic fillers that are generic: They can be customized to some extent, but they might not be able to solve all issues.
Surgical implants:
May not be as easily customized or adjusted to changes in the patient’s look over time, and they are typically more permanent.
Conclusion:
In summary, stem cells are an exciting area of biology that could completely transform medical practice. Their special qualities provide hope for novel therapies and remedies for a variety of illnesses and ailments. To fully grasp their potential and solve the safety and ethical issues raised by their use, more research is necessary.
Stem cells provide a window into the potential for treating diseases at their source and regenerating damaged tissues in medicine. The potential of stem cells to change healthcare and improve lives is genuinely endless as research and technology develop.
- All Posts
- Uncategorized

Dr. Daniel Davidson, MD, MBA Introduction: The goal of success for businesses nowadays is to establish a global brand because…

Dr. Daniel Davidson, MD, MBA Introduction: Stem cells have captivated the imagination of scientists and the public alike for their…

Dr. Daniel Davidson, MD, MBA Introduction: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP), fat grafting, and dermal fillers made from natural sources are examples…
