Introduction:
Clinics that perform plastic surgery are using technology more and more to improve patient care, increase operational effectiveness, and boost revenue. Technology is completely changing the way plastic surgery clinics run and engage with their patients. Examples of these innovations include cutting-edge imaging equipment and digital marketing tactics. This article examines how technology has a significant impact on plastic surgery clinics and how it helps them succeed as a company.
Virtual Consultations with Telemedicine:
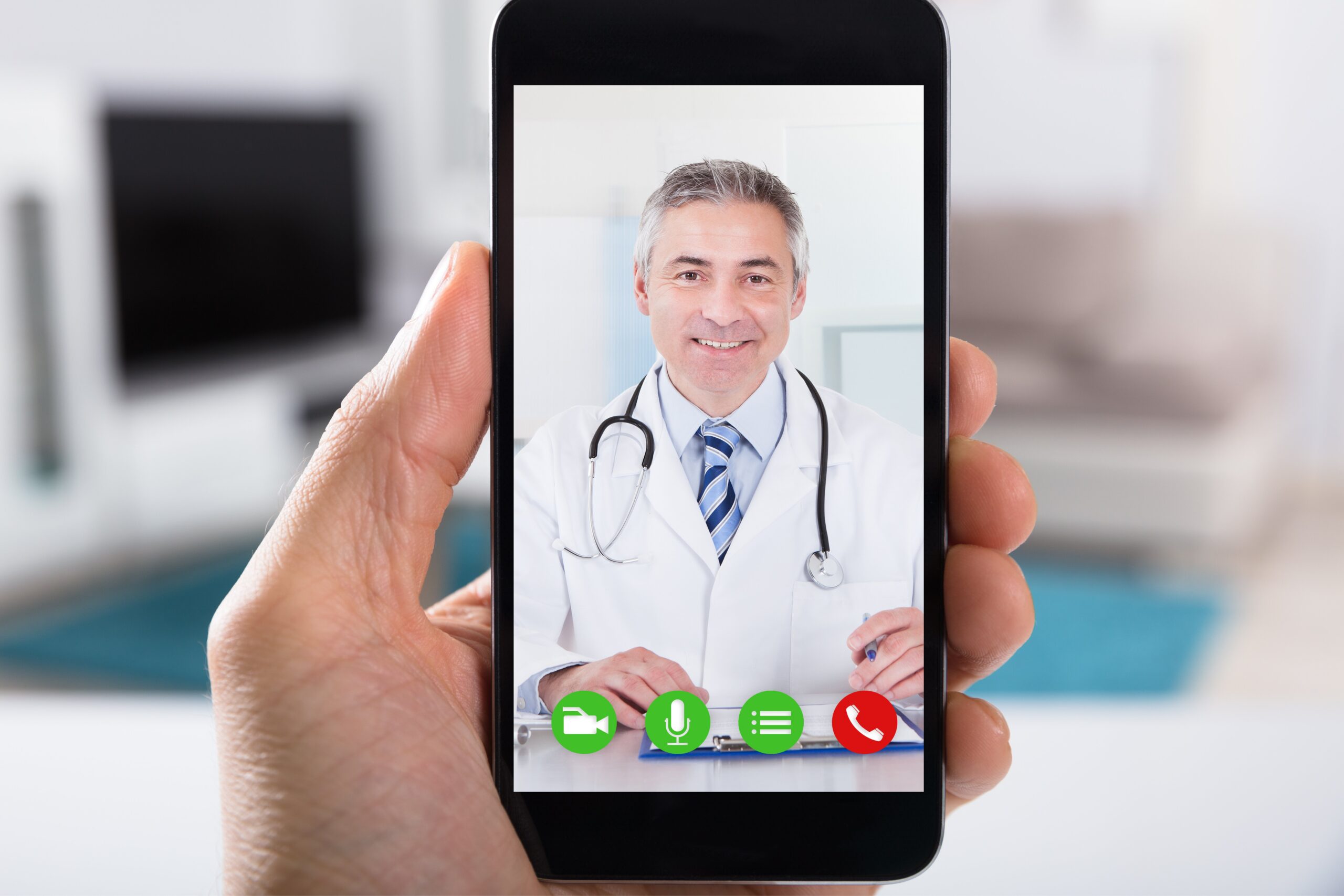

Combining virtual consultations with telemedicine has proven to be a revolutionary move for plastic surgery practices. By removing regional restrictions, prospective patients can now communicate with surgeons virtually, increasing the clinic’s reach. This creates new opportunities for corporate expansion in addition to making the patient experience more convenient.
Advanced Imaging and Simulation: With the advent of advanced imaging and simulation equipment, technology has completely changed the consultation procedure in plastic surgery clinics. With the use of these technologies, surgeons can produce incredibly accurate three-dimensional (3D) models of their patients’ anatomy, which helps them to simulate various treatment choices and see possible surgical outcomes. Advanced imaging and simulation systems improve communication, foster trust, and raise patient satisfaction by giving patients a realistic preview of their findings. This promotes better decision-making and higher conversion rates.
Electronic Health Records Systems:
Plastic surgery clinics can reduce administrative workloads by implementing EHR systems. EHR systems reduce paperwork and mistake risk by improving operational efficiency in a variety of areas, including appointment scheduling and patient record management. This improved structure facilitates a more efficient process, which eventually helps the clinic succeed.
The use of robotics in plastic surgery treatments is a major advancement in safety and precision. Surgical robotics improves overall patient outcomes, speeds up recovery from complex surgeries, and allows for more accuracy in less time. Robotic-equipped plastic surgery clinics draw patients looking for state-of-the-art methods and maintain a leading position in the medical field.
Multimedia-Based Patient Education:
Using multimedia tools, technology makes complete patient education possible. Patients can have a deeper understanding of operations, hazards, and recovery processes with the use of instructional apps, interactive presentations, and animated movies. Well-informed patients are more likely to make decisions with assurance, which raises satisfaction and encourages positive word-of-mouth recommendations.
The use of diverse multimedia, including films, animations, interactive presentations, and digital resources, to teach patients about their medical issues, available treatments, and self-care techniques is known as multimedia-based patient education. By using interactive and visual components, this method makes information easier to understand and more engaging for patients, enabling them to actively participate in their health management and make educated decisions.
Safe Data Management and Compliance:
As patient records and sensitive data become more digitally digitized, it is critical to make sure that strong data security and privacy laws are followed. Utilizing technology to establish safe data management procedures helps plastic surgery practices gain the patient trust that is necessary for sustained success and goodwill.
Safe data management and compliance, especially in the context of healthcare, refers to the procedures and guidelines that businesses have put in place to guarantee the security, privacy, accuracy, and compliance of sensitive data. An outline of safe data handling and compliance procedures is provided below:
Data Encryption:
During transmission and storage, sensitive data, including patient health information (PHI), is protected via encryption techniques used by organizations. Encryption protects data from unwanted access by transforming it into unintelligible representations that can only be read with special decryption keys.
Access Controls:
Using the least privilege principle, access controls limit who has access to sensitive information. This implies that the minimal amount of data required for employees to carry out their duties is only accessible to those who are permitted. Role-based access control (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and user authentication are examples of access controls.
Secure Storage:
Sensitive data, such as electronic health records (EHRs) and other medical documents, must be kept in secure locations by organizations. This could entail making use of safe servers, secured databases, and cloud storage options.

Frequent Audits and Monitoring:
Organizations can detect and reduce any security risks and compliance problems with the aid of regular audits and monitoring. This include keeping an eye on access logs, evaluating the security of the system, and running vulnerability scans to find and fix any infrastructure flaws quickly.
Regulation Compliance:
Healthcare institutions are required to abide by laws and guidelines protecting the privacy and security of patient data, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the US. Ensuring regulatory compliance and protecting patient data through the implementation of policies, processes, and technological protections is the essence of compliance.
Practice Management Software:
Software called practice management is intended to assist medical professionals in organizing and managing their administrative duties and running their practices more efficiently. It has a number of features and capabilities designed to meet the requirements of healthcare facilities, including clinics, hospitals, and doctor’s offices. An outline of practice management software’s main elements is provided below:
Appointment Scheduling:
Healthcare professionals can effectively plan patient appointments with the use of practice management software. Real-time scheduling management, availability viewing, and appointment scheduling are all available to providers. In order to lower the number of no-shows, several software programs additionally provide automated appointment reminders.
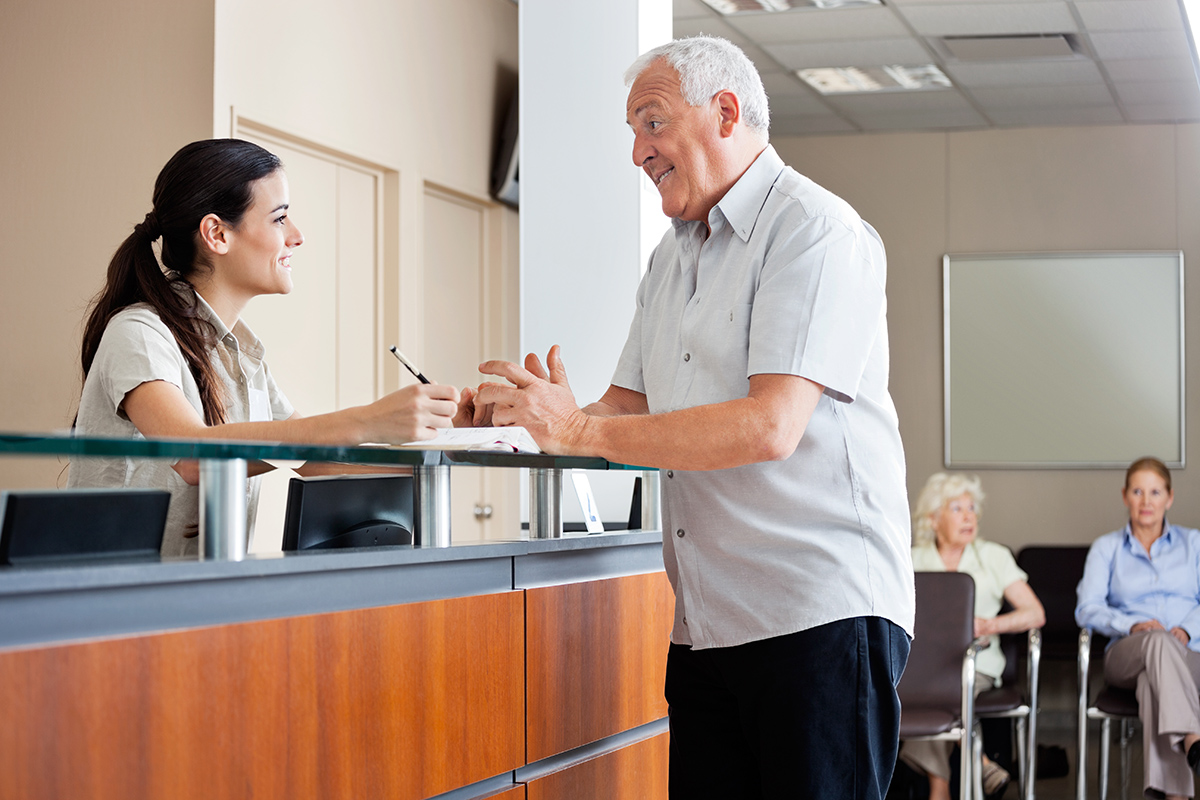

Patient Check-In and Registration:
By electronically recording insurance information, medical history, and demographic data, practice management software expedites the patient check-in procedure. Patients can lessen the amount of paperwork and administrative strain by completing registration forms online or at self-service kiosks.
Billing and Claims Management:
By automating billing procedures, producing invoices, and electronically submitting insurance claims, practice management software makes billing and claims management activities easier. It facilitates revenue cycle management, patient account administration, and payment tracking for providers.
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR):
A lot of practice management software programs include a smooth integration with EHR systems, which makes it possible for clinical and administrative staff to share patient data with one another. Through this integration, data input duplication is decreased, communication is improved, and care coordination is improved.
Practice management software facilitates the tracking of key performance indicators (KPIs), analysis of practice trends, and financial performance of providers through the provision of reporting and analytics tools. To aid in decision-making and increase practice efficiency, users can create customized reports on patient demographics, income, appointment use, and other variables.
Conclusion:
Technology has a significant influence on plastic surgery clinics outside of the operating room. Accepting these technology developments puts clinics in a position for long-term success in a market that is becoming more and more competitive while also improving patient care and results. Technology is the engine propelling the progress of plastic surgery practices, guaranteeing that clinics stay at the forefront of innovation and excellence from optimizing operations to reaching a wider audience. Future prospects for plastic surgeons and their patients are promising as long as the mutually beneficial relationship between technology and plastic surgery persists.
- All Posts
- Uncategorized

Dr. Daniel Davidson, MD, MBA Introduction: The goal of success for businesses nowadays is to establish a global brand because…

Dr. Daniel Davidson, MD, MBA Introduction: Stem cells have captivated the imagination of scientists and the public alike for their…

Dr. Daniel Davidson, MD, MBA Introduction: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP), fat grafting, and dermal fillers made from natural sources are examples…
