Introduction:
Restoring hair growth in scalp areas impacted by thinning or hair loss is the goal of hair transplant surgery, a cosmetic technique. Hair transplantation has a few decades of history and has progressed from crude techniques to advanced technologies that provide outcomes that resemble natural hair. We will explore the fascinating background, standard protocol, different approaches, advantages, and drawbacks of hair transplant surgery in this post.
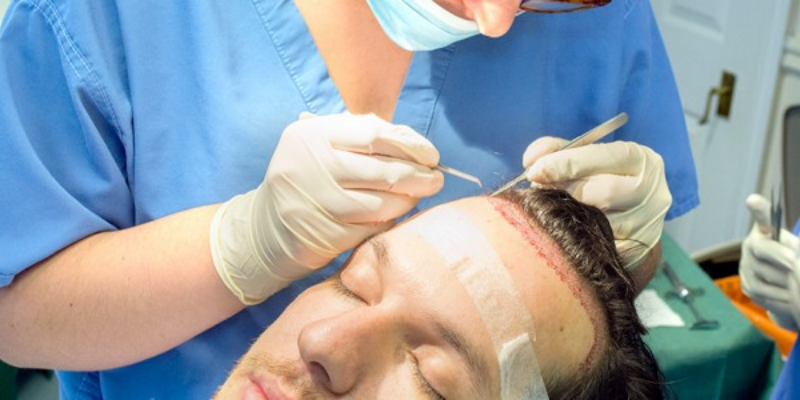
History of hair transplant:
Dr. Shoji Okuda, a dermatologist from Japan, was one of the first people to perform hair transplants. Dr. Okuda released a ground-breaking study in 1939 outlining a method for grafting tiny skin grafts containing hair follicles onto scalp regions that were balding. The “punch graft method,” as this procedure is called, served as the model for contemporary hair transplantation.
New York City dermatologist Dr. Norman Orentreich made significant advancements in the field of hair transplantation during the 1950s and 60s. Hair follicles from the donor area—the back and sides of the scalp—were resistant to the effects of baldness and could be transplanted to balding parts of the scalp without being rejected, according to Dr. Orentreich’s research.
Surgeons started creating novel methods for hair transplantation, such as using smaller grafts and more exact follicle placement, based on the work of Dr. Orentreich. These developments resulted in the creation of the “strip harvesting” procedure, which involves transplanting a strip of skin containing hair follicles from the donor location to the balding area.
Further advancements in hair transplantation methods were made in the 1990s and 2000s, with the development of follicular unit extraction (FUE) and transplantation (FUT). These methods made it possible to transplant individual hair follicles, which produced outcomes that looked more natural and required less time to heal.
Millions of hair transplant treatments are carried out annually throughout the world as a well-recognized and very successful treatment for hair loss. The results of hair transplantation are getting better thanks to advancements in technology and surgical methods, which is why more and more people are choosing this option to regain their confidence and hair.
Procedure in general
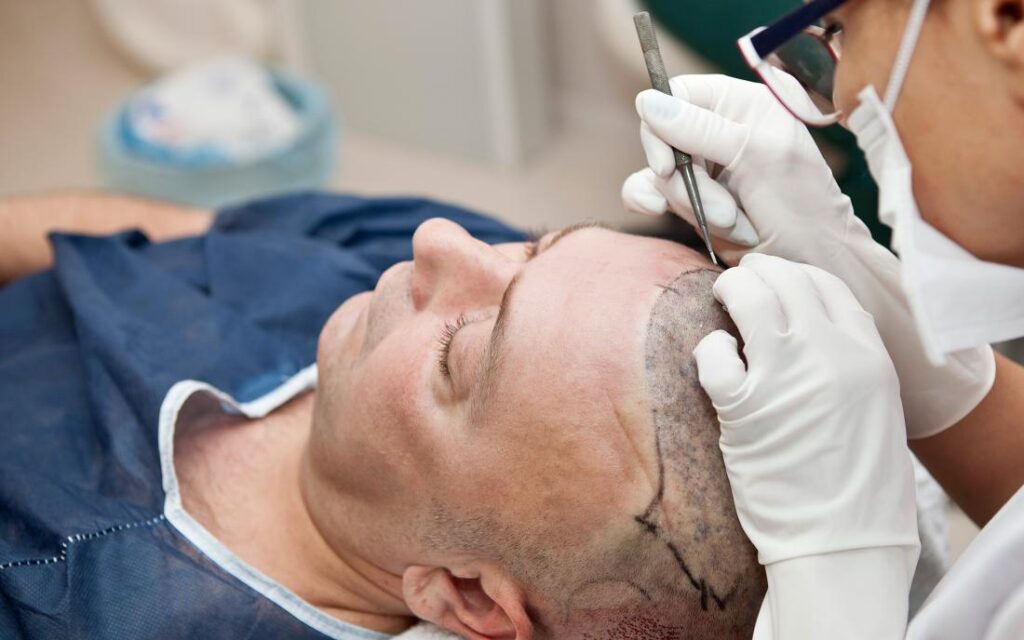
In order to reduce discomfort during the surgery, the patient’s scalp is washed and given a local anesthetic before the treatment. Additionally, the donor area—typically the sides or back of the head, where the hair is thicker and less prone to balding—is prepped for the extraction of hair follicles.
Getting the Recipient Site Ready:
After the hair follicles are extracted, the surgeon makes the small scalp incisions or holes necessary for the follicle transplant. For the incisions to appear natural, the placement is essential.
Hair Follicle Transplantation:
The recipient areas are properly seeded with the harvested hair follicles. Depending on the approach employed, the surgeon may implant the follicles manually or with the aid of a specific tool.
Post-Operative Care:
The patient may receive instructions on how to take care of their scalp and newly transplanted hair, and their scalp may be bandaged following the transplant. After the treatment, some soreness and swelling are normal, but these side effects usually go away in a few days or weeks.
Follow-up:
Patients are often arranged for follow-up consultations in order to track the development of their hair growth and to answer any queries or issues they may have.
Preoperative Evaluation: To ascertain the patient’s suitability for surgery, the surgeon evaluates the patient’s scalp, hair density, and availability of donor hair.
Various techniques
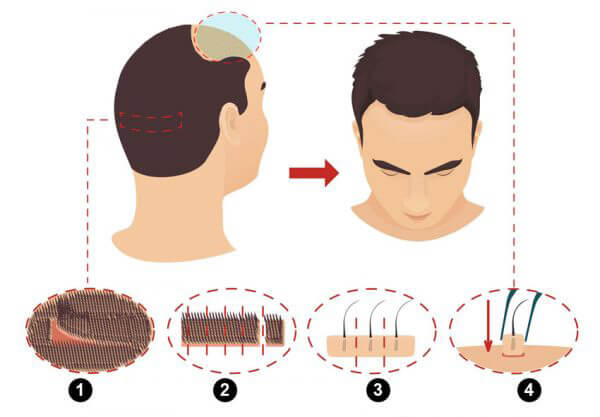
Transplantation of Follic Units (FUT):
FUT, sometimes referred to as the strip procedure, entails taking a strip of skin from the donor region, which is often the sides or back of the scalp, and using a microscope to separate it into individual follicular units.
After that, the recipient sites get the transplanted follicular units.
FUT is appropriate for people who need substantial hair restoration since it can transplant a high number of grafts in a single session.
Extraction of Follic Units (FUE):
Using a tiny device that resembles a punch, FUE involves removing individual follicular units straight from the donor region.
The recipient sites are subsequently seeded with the follicular units.
Compared to FUT, FUE requires less scarring and a shorter recovery period because it does not require a linear incision. It might, however, cost more money and take more time.
Hair Implantation Directly (DHI):
Using a specialized instrument known as a Choi implanter pen, the follicular units are removed and implanted simultaneously in a version of FUE known as DHI.
With this method, the angle, depth, and direction of the implanted hairs may be precisely controlled, producing an appearance that is more natural.
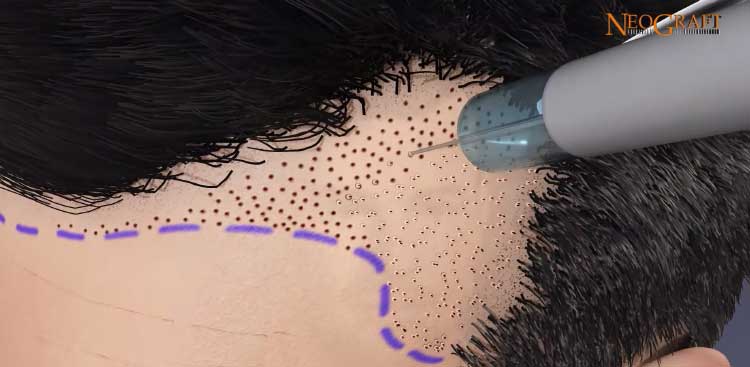
Automated Hair Replacement:
Hair follicles are harvested and transplanted using a robotic device in robotic hair transplantation.
By utilizing algorithms to locate and extract the best follicular units, the method lowers the possibility of human error and increases procedure precision overall.
Therapy Using Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP):
A tiny amount of the patient’s blood is extracted for PRP therapy, which subsequently comprises processing the blood to concentrate the platelets and injecting the PRP into the scalp.
Prosthetic root grafting (PRP) is a common add-on for hair transplant surgeries since it is thought to stimulate hair growth and enhance scalp health in general.
Micropigmentation on the Scalp (SMP):
SMP is a non-surgical technique that imitates thicker hair using certain pigments.
When combined with other hair restoration procedures, it is frequently used to conceal scars from prior hair transplant surgery or to provide the appearance of a thicker head of hair.
Benefits, Comparisons, and Considerations:
Depending on the patient’s desired outcome, scalp condition, and pattern of hair loss, each hair transplant technique has unique advantages and considerations. While FUE offers less scarring and a quicker recovery period, making it excellent for patients with shorter hair or those who wish to wear their hair short, FUT may produce a higher yield of grafts and is appropriate for individuals with bigger areas of hair loss. While multi-follicular transplantation offers better coverage and density but may provide a somewhat less natural appearance, unifollicular transplantation offers accurate placement and outcomes that look natural, but may need more time and skill from the surgeon. Although obsolete, plug transplantation may be appropriate for some patients with particular patterns of hair loss, although there is a greater chance of visible scarring.
Transplantation of Follic Units (FUT):
Benefits: FUT is appropriate for patients who need substantial hair restoration since it can transplant a high number of grafts in a single session. Because they have had little handling, the harvested grafts typically have great survival rates.
Comparisons: FUT leaves a linear scar in the donor location that may show if the patient has short hair. The incision is made linearly. Due to the requirement for sutures, recovery times may be greater than with other methods.
Consideration:
FUT can be the better option for people who need a lot of grafts and don’t mind having a straight scar in the donor area.
FUE, or Follicular Unit Extraction:
Benefits:
Compared to FUT, FUE requires less scarring and a shorter recovery period because it does not require a linear incision. It can be utilized to harvest hair from various places of the body and gives more flexibility in transplant placement.
Comparisons:
Because each follicular unit must be harvested individually, FUE may require more time and money than FUT. Patients with narrow scalps or significant hair loss may also find the surgery less appropriate.
Considerations:
FUE might be chosen for patients who want the least amount of scarring, have a shortage of donors, or need grafts to be taken from unusual places.
Hair Implantation Directly (DHI):
Advantages:
DHI provides exact control over the implanted hairs’ angle, depth, and orientation, making the final result appear more realistic. By cutting down on the amount of time between graft extraction and implantation, the method lowers the possibility of graft deterioration.
Comparisons:
Because DHI requires specific equipment and knowledge, it may be more expensive than other procedures. Depending on how many grafts are being transplanted, the process could possibly take longer.
Considerations:
Patients who value natural-looking outcomes and are prepared to spend money on cutting-edge tools and methods might find that DHI is their first choice.
Automated Hair Replacement:
Benefits:
By eliminating human error in graft harvesting and implantation, robotic hair transplantation provides accuracy and consistency. High-quality grafts can be produced by precisely identifying and extracting the ideal follicular units using the method.
Comparisons:
Because of the expense of the robotic device, robotic hair transplantation may be more costly than manual methods. The size and form of the donor area that the robot may access may also place restrictions on the operation.
Considerations:
Patients who value accuracy and are prepared to spend money on cutting-edge technology may find that robotic hair transplantation is their preferred method. Additionally, people with particular patterns of hair loss that respond well to robotic aid may find it appropriate.
Treatment using Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP):
Benefits:
PRP treatment might enhance scalp health overall and encourage hair growth. To improve outcomes, it can be applied alone or in conjunction with other hair restoration methods.
Comparisons:
PRP therapy effects can differ from patient to patient and may need several sessions to yield the best results. Though generally safe, there is a chance of some mild discomfort and transient swelling at the injection site.
Points to consider:
Patients who want to improve the outcome of their hair transplant surgery or who are not candidates for surgical hair restoration may find that PRP therapy is the better option. Additionally, it might be helpful for individuals who are experiencing early-stage hair loss or as a prophylactic against additional hair loss.
Complications and Risks:
Hair transplant surgery has certain risks and potential complications, such as the following, but is normally safe when carried out by a trained and experienced surgeon.
Bleeding Infection
Soreness or numbness on the scalp
Damage
inadequate graft growth or survival
transient shock loss, or the transient loss of hair transplants
Inadequate aesthetic results
Conclusion:
People who are experiencing hair loss now have a permanent remedy with hair transplant surgery that restores confidence and produces results that seem natural. In the hands of a knowledgeable and competent hair transplant surgeon, patients can make educated decisions and attain satisfactory results by being aware of the background, general process, different procedures, and related issues of the treatment. A customized treatment plan that addresses each patient’s specific requirements and desired aesthetic results must be developed during the consultation process. Individual goals, concerns, and expectations must be discussed.
- All Posts
- Uncategorized

Dr. Daniel Davidson, MD, MBA Introduction: The goal of success for businesses nowadays is to establish a global brand because…

Dr. Daniel Davidson, MD, MBA Introduction: Stem cells have captivated the imagination of scientists and the public alike for their…

Dr. Daniel Davidson, MD, MBA Introduction: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP), fat grafting, and dermal fillers made from natural sources are examples…
